
DOC023.98.90594
AN-ISE sc, AISE sc, NISE sc probe
Addendum—Operation with the SC1500 Controller
05/2017, Edition 1


3
Table of contents
English..................................................................................................................................................... 5
Deutsch.................................................................................................................................................. 23
Español.................................................................................................................................................. 41
Français ................................................................................................................................................. 59
Italiano ................................................................................................................................................... 79
Nederlands ............................................................................................................................................ 97
Dansk ................................................................................................................................................... 115
Polski ................................................................................................................................................... 133

4
Table of contents

English 5
Section 4 Operation
English
For more information on System Setup (current outputs, relays, and
network interfaces), refer to the sc1500 User Manual.
The following tables show the sensor menu for the AN-ISE sc
probe, AISE sc probe and NISE sc probe. If a menu item does not
apply to all three probes, its applicability is explained in footnotes.
Footnote
1 indicates applicability to the AN-ISE sc probe. The
AN-ISE sc probe is used to determine the ammonium and nitrate
concentration, as well as the potassium and chloride concentration.
Footnote
2 indicates applicability to the AISE sc probe. The AISE sc
probe is used to determine the ammonium and potassium
concentration.
Footnote
3 indicates applicability to the NISE sc probe. The NISE sc
probe is used to determine the nitrate concentration and chloride
concentration.
4.1 Sensor diagnostics menu
SENSOR STATUS
AN-ISE sc or AISE sc or NISE sc
Error list Shows all current error messages.
Warning list Shows all current warnings.
4.2 Sensor setup menu
SELECT AN-ISE sc or AISE sc or NISE sc (if more than one sensor or analyzer is attached)
Calibration
Matrix correction
Matrix correction options.
The most recently used menu is displayed.
The currently active corrections are shown in Information.
None No Matrix corrections activated
1-point matrix correction 1-point matrix correction
NH
4
+ NO
3
1
1-point matrix correction for ammonium and nitrate
NH
4
1,2
1-point matrix correction for ammonium
NO
3
1,3
1-point matrix correction for nitrate
NH
4
+ K
1,2
1-point matrix correction for ammonium and potassium
NO
3
+ Cl
1,3
1-point matrix correction for nitrate and chloride
NH
4
+K + NO
3
+Cl
1
1-point matrix correction for ammonium, potassium, nitrate and chloride
Take the grab sample
immediately for the lab
analysis.
Information window: When this window appears, the sample must be taken immediately
and then analyzed in the laboratory.
1-point value correction
Perform 1-point value correction.
The most recently used menu is displayed.
The currently active corrections are shown in Information.
NH
4
–N
1
Select parameter for the 1-point value correction
NO
3
–N
1
Enter the values for the
first point
Enter the values for the 1-point value correction
Note: The following example shows the input when using a AN-ISE sc probe for
ammonium. When using the AISE sc probe, the input is the same. When using the
NISE sc, it is only possible to input the nitrate and chloride values.

6 English
Operation
Calibration (continued)
AN-ISE SC NH
4
–N Enter the displayed ammonium value
AN-ISE SC K Enter the displayed potassium value
Lab value NH
4
–N Enter the laboratory ammonium value
Confirm the entry. Confirm the values entered
Correction result Display the correction results
2-point value correction Perform 2-point value correction
NH
4
–N
1
Select parameter for the 2-point value correction
NO
3
–N
1
Enter the values for the
first point
Enter the values for the 2-point value correction (first point)
Note: The following example shows the input when using a AN-ISE sc probe for
ammonium. When using the AISE sc probe, the input is the same. When using the
NISE sc, it is only possible to input the nitrate and chloride values.
AN-ISE SC NH
4
–N Enter the displayed ammonium value
AN-ISE SC K Enter the displayed potassium value
Lab value NH
4
–N Enter the laboratory ammonium value
Confirm the entry. Confirm the values entered
Enter the values for the
second point.
Enter the values for the 2-point value correction (second point).
Note: The following example shows the input when using a AN-ISE sc probe for
ammonium. When using the AISE sc probe, the input is the same. When using the
NISE sc, it is only possible to input the nitrate and chloride values.
AN-ISE SC NH
4
–N Enter the displayed ammonium value
AN-ISE SC K Enter the displayed potassium value
Lab value NH
4
–N Enter the laboratory ammonium value
Confirm the entry. Confirm the values entered
Correction result Display the correction results
More corrections Other matrix correction options
None No More corrections is activated
2-point matrix correction A 2-point matrix correction can be performed here
NH
4
1
Parameter selection for the 2-point matrix correction.
NO
3
1
Concentration
measurement 1
Saves the currently measured measurement for the first point
Date Displays the date of the current correction of the first point
Concentration 1 Entry and display of reference value for the first point
Concentration
measurement 2
Saves the currently measured measurement for the second point
Date Displays the date of the current correction of the second point
Concentration 2 Entry and display of the reference value for the second point
Previous corrections Selection of one of the last corrections performed
Sensor code The sensor code can be activated or entered here
Activate Activates the sensor code for the individual channels
NH
4
+ K
1
Activate the sensor code for ammonium and potassium
NO
3
+ Cl
1
Activate the sensor code for nitrate and chloride
NH
4
+K + NO
3
+Cl
1
Activate the sensor code for ammonium, potassium, nitrate and chloride
Reset calibration Activates factory calibration
4.2 Sensor setup menu (Continued)

English 7
Operation
Calibration (continued)
Sensor code Entry of the sensor code
Lab value correction The laboratory values of the last matrix correction can be changed
Enter the lab value.
Enter the laboratory values if 1-point matrix correction or 2-point matrix correction has
been selected
Ammonium
1,2
Entry of ammonium laboratory value
Nitrate
1,3
Enter the laboratory value for nitrate
Potassium
1,2
Enter the laboratory value for potassium
Chloride
1,3
Enter the laboratory value for chloride
Confirm the entry. Confirm the values entered
Correction result Display the correction results
NH
4
–N
1,2
Displays whether or not the ammonium correction was successful
NO
3
–N
1,3
Shows whether or not the nitrate correction was successful
K+
1,2
Displays whether or not the potassium correction was successful
Cl
1,3
Displays whether or not the chloride correction was successful
Information Information on the matrix correction used per parameter
NH
4
–N
1,2
Matrix correction used for ammonium
NO
3
–N
1,3
Matrix correction used for nitrate
K+
1,2
Matrix correction used for potassium
Cl
1,3
Matrix correction used for chloride
Settings
Name
Enter or edit the name.
Up to 10 alphanumeric characters
Unit Select either mg/L or ppm as the measurement unit
Parameter Select NH
4
–N or NH
4
and/or NO
3
–N or NO
3
Temperature Selection of °C or °F as temperature unit
Offset temperature Enter a temperature offset
Response time Entry of the response time (30 sec to 300 sec)
Datalog interval
Select the data log interval (OFF, 30 sec, 1 min, 2 min, 5 min, 10 min, 15 min and
30 min), 5 min is the factory setting
K+ compensation
1,2
Select automatic potassium compensation:
On
Off
0 = compensation OFF
0.1–2000 mg/L Cl = Fixed compensation value
K+ concentration
1,2
Only shown when K+ COMPENSATE is OFF
Cl - compensation
1,3
Select automatic chloride compensation:
On
Off
0 = compensation OFF
0.1–2000 mg/L Cl = Fixed compensation value
Cl - concentration
1,3
Only shown when Cl COMPNSATE is OFF
Reset configuration Resets the configuration to the factory setting
Maintenance
Sensor information Information on the connected sensor
Sensor type Name of the connected sensor
4.2 Sensor setup menu (Continued)

8 English
Operation
Maintenance (continued)
Name Serial number or name of the measurement location
Serial number Serial number of the connected sensor
Sensor type Instrument designation of the connected sensor
Software Software version
Calibration history
Data of the selected matrix correction and information about slope and offset of the
individual channels, for example
NH
4
–N
1,2
Matrix correction selected for ammonium
NO
3
–N
1,3
Matrix correction selected for nitrate
K+
1,2
Matrix correction selected for potassium
Cl
1,3
Matrix correction selected for chloride
Signals Signals and measurement results of the individual measurement channels
Ammonium
1,2
Display the signals and measurement results for ammonium
Nitrate
1,3
Shows the signals and measurement results for nitrate
Potassium
1,2
Display the signals and measurement results for potassium
Chloride
1,3
Display the signals and measurement results for chloride
Reference electrode Displays the signals and measurement results for the reference system
mV RAW Display the signals and measurement results for MV RAW
Impedance status Display the signals and measurement results for impedance
Temperature Display the signals and measurement results for temperature
Moisture Display the signals and measurement results for humidity
RFID Display the signals and measurement results for RFID
Last calibration Shows the age of the last matrix correction
Ammonium
1,2
Display the age of the last matrix correction for ammonium
Nitrate
1,3
Display the age of the last matrix correction for nitrate
Service
Cartridge test Perform a sensor check with the test cartridge
Cartridge test Display whether the individual sensor channels are OK or not
Maintenance Displays whether or not DIAG/TEST is OK
Ground rod Displays whether or not GNDROD is OK
Reference electrode Displays whether or not REF channel is OK
NO
3
1,3
Displays whether or not NO3 channel is OK
NH
4
1,2
Displays whether or not NH4 channel is OK
ORP Displays whether or not ORP channel is OK
Cl-
1,3
Shows whether or not Cl channel is OK
K+
1,2
Displays whether or not K channel is OK
Temperature Displays whether or not temperature channel is OK
Cartridge replacement Follow the menu process
Cleaning... Follow the menu process
1
Applies to AN-ISE sc
2
Applies to AISE sc
3
Applies to NISE sc
4.2 Sensor setup menu (Continued)

English 9
Operation
4.3 Calibration/matrix correction
The four electrodes with the reference system of the compact
sensor cartridge were calibrated with one another at the factory
using special standard solutions (CARTICAL
TM
). However, the
membranes on the ion-selective electrodes are not 100% selective
due to other substances that may affect the measurement. Perform
a matrix correction (refer to 4.3.4, page 11) to compensate for other
ions present on the ISE electrodes.
Potassium has the largest interference effect on the ammonium
membrane, while chloride has the largest effect on the nitrate
membrane. The AN-ISE sc probe compensates for this problem
with the aid of a built-in potassium/chloride electrode.
When using the AISE sc probe, only the ammonium membrane and
the integrated potassium electrode are active.
When using the NISE sc probe, only the nitrate membrane and the
integrated chloride electrode are active.
Cross sensitivities between ammonium and potassium/nitrate are
automatically eliminated. Solids do not interfere with the
measurement. Due to matrix effects, correction and validation
cannot be performed with standard solutions. A matrix correction
can be carried out quickly and easily at any time.
4.3.1 Sensor code calibration
The sensor code is a calibration code and is delivered with the
sensor cartridge certificate. It contains the factory calibration
described in section 3.12, page 9 for the sensor cartridge.
Instruments with automatic sensor code recognition
(LXG440.99.x000x) read this automatically and assume the
Cartrical calibration.
Instruments without automatic sensor code recognition
(LXG440.99.x001x) require the sensor code to be entered during
the initial setup and whenever a new sensor cartridge is activated. If
the sensor code certificate has been lost, carry out factory
calibration (under the sensor code menu) as a temporary solution.
After activating the code, the sensor is fully calibrated but not yet
adapted to the specific matrix of the relevant application on a waste
water treatment plant. At least 12 hours must elapse before a
matrix correction is performed to allow the cartridge to adapt to the
specific matrix.
NOTICE
A matrix correction may only be performed if the sensor has been
immersed in the corresponding waste water matrix for over 12 hours.
This is the minimum time required to adapt the ISE membranes to the
waste water matrix.

10 English
Operation
Proceed as follows to change the sensor code:
1. Select
SENSOR MENU > AN-ISE SC or AISE SC or NISE SC >
CALIBRATION > MORE CORRECTIONS> SENSOR CODE >
ENTER
2. Enter the sensor code.
3. Press
ENTER to confirm and activate the sensor code. The day
meter for the cartridge is set to zero.
All old calibration data are now overwritten with the new calibration
data from the sensor code. The sensor code data is checked by the
system. If an error is indicated, check the sensor code and, if
necessary, enter the sensor code again.
4.3.2 Matrix correction via LINK2SC
The LINK2SC procedure offers a secure method of data exchange
between process probes and LINK2SC-compatible photometers
using an SD memory card or via a local area network (LAN). Two
different options are available:
a. The pure laboratory control measurement
b. A matrix correction that involves the measurement data
generated in the laboratory being used to correct the probe
During a pure control measurement, the measurement data is
transferred from the probe to the photometer where it is then
archived together with the photometric reference data that has
been recorded.
During a matrix correction, the reference data generated in the
laboratory is transferred to the probe to be used for the correction.
The matrix correction process requires operating steps to be
completed on the sc controller and on a LINK2SC-compatible
photometer.
Refer to the LINK2SC user manual for a detailed description of the
LINK2SC procedure.
When using the LINK2SC software, sections 4.3.3 and 4.3.4 are
not relevant.
4.3.3 Matrix correction – manual
ISE probes offer different options (refer to Table 1) for correcting
the sensor value with laboratory values (as a reference value).
The laboratory value of the water sample is entered as nitrate
nitrogen (NO
3
–N) and/or as ammoniacal nitrogen (NH
4
–N). This
laboratory value replaces the prior value measured by the sensor.

English 11
Operation
4.3.4 Performing the matrix correction
Note: Take laboratory value measurements or reference values promptly
or, alternatively, take these from the stabilized sample. This will prevent
changes in sample concentration, as time is a factor in comparative tests.
Refer to 7.3 Validation accessories, Page 39 for recommended
laboratory measurement tests.
4.3.4.1 1-point matrix correction
Proceed as follows to perform 1-point matrix correction:
1. Select
SENSOR MENU > AN-ISE SC or AISE SC or NISE SC >
CALIBRATION > 1-point matrix correction
.
2. Select
2-point matrix correction from the selection window and
press
ENTER.
3. Select the parameters you wish to correct and confirm by
pressing
ENTER.
Selection options for AN-ISE sc:
NH
4
+ NO
3
; NH
4
; NO
3
; NH
4
+ K; NO
3
+ Cl; NH
4
+ K NO
3
+ Cl
Selection options for AISE sc:
NH
4
; NH
4
+ K
Table 1 Correction options for ISE probes
Correction option Application
1-point matrix
correction
A 1-point matrix correction is the most commonly used correction option and performs a 1-point
matrix correction for ammonium and/or nitrate (4.3.4.1, page 11). It is advisable to perform a 1-point
matrix correction as the first correction. The 1-point matrix correction can be performed both with
and without correction of the compensation electrodes (potassium or chloride); in most cases, it is
sufficient to perform it without correction. A correction featuring potassium and/or chloride is only
necessary if a high level of accuracy is required. With a 1-point matrix correction, a sample must be
taken when the correction is triggered and analyzed in the laboratory. The 1-point matrix correction is
activated when the laboratory value is entered.
1-point value
correction
1-point value correction (correction at one concentration point) corresponds to a 1-point matrix
correction with an alternative entry format.
Comparison values between the ISE probe and the laboratory can be collected over a period of
around a week with this correction. The correction can be performed at a later stage.
2-point value
correction
2-point value correction (correction at 2 different concentration points) should be performed if
dynamic concentration fluctuations are present over at least half a decade
1
and a 2-point
matrix correction or 1-point value correction does not achieve a sufficiently accurate result.
Comparison values between the ISE probe and the laboratory can be collected over a period of
around a week with this correction. The correction can be performed at a later stage.
2-point matrix
correction
The 2-point matrix correction corresponds to a 2-point value correction, but uses an
alternative entry format and is recommended if there is a dynamic process with a large
nitrate/ammonium fluctuation greater than at least half a decade
1
. With a 2-point matrix correction, a
sample must be taken for both points when the correction is triggered and analyzed in the laboratory.
The 2-point matrix correction is activated when the laboratory value is entered.
Previous corrections
Return to one of the last matrix and value corrections performed if a correction has not produced
a successful result.
1
Examples of half a decade: The concentration of nitrogen nitrate shifts between 1 and 5 mg NO
3
–N or
between 5 and 25 mg/L NO
3
–N. (conc2 = (conc1 x 10)/2)
Calibration
Matrix correction
More corrections
Information

12 English
Operation
Selection options for NISE sc:
NO
3
; NO
3
+ Cl
The sensor saves the current values of the selected parameters at
this point.
4. Take a water sample immediately from the closest point
possible to the sensor. Filter the sample as quickly as possible
and carry out a prompt laboratory analysis of the selected
parameters, as the measurement value can change quickly.
When the laboratory value has been determined, proceed as
follows:
5. Select SENSOR MENU > AN-ISE SC or AISE SC or NISE SC
> CALIBRATION > Enter the lab value.
6. The laboratory values for the parameters can only be entered if
the 1-point matrix correction correction has been selected
beforehand. Once the laboratory values have been entered,
select Confirm the entry. to confirm.
When the entered laboratory value is confirmed, the matrix
correction is activated.
7. Once the correction is activated, the result Correction result is
shown.
Note: This process must always be carried out in full to make sure the
matrix correction is completed successfully.
If a correction does not produce a successful result, calculations are made
with the previous correction.
4.3.4.2 1-point value correction
The 1-point value correction offers the option of retrospectively
performing a matrix correction at one point.
1. Take several samples with different concentrations on various
days, preferably within one week. Analyze the samples in the
laboratory. During the time the samples are being taken, the
sample temperature should vary a maximum of 5 °C, as
temperature changes are not taken into account in the value
correction.
2. Make a note of the two values measured in the samples and
displayed for the parameters to be corrected (ammonium and
potassium values, or nitrate and chloride values)
3. Also note the laboratory values measured for ammonium or
nitrate.
These three values form the correction point.
4. From the values taken, select a correction point that lies in the
middle of the expected concentration range.
1-point matrix
correction
Take the grab sample
immediately for the lab
analysis.
Calibration
Matrix correction
More corrections
Enter the lab value.
Information
Calibration
Matrix correction
More corrections
Information

English 13
Operation
5. Go to the sensor menu and select CALIBRATION > MATRIX
CORRECTION >
1-point value correction and confirm by
pressing
ENTER.
6. Select the parameter1 (NH
4
–N or NO
3
–N) that requires
correction.
Note: The example opposite shows the NH
4
-N and K correction of the
AN-ISE sc probe.
7. Enter the three values for the sought correction point and push
Confirm the entry. to activate the correction.
Correction result is shown.
Note: If a correction does not produce a successful result, calculations are
made with the previous correction.
After successful completion of value correction, the corrected value is
shown as the display value for ammonium or nitrate the next time the menu
is opened.
4.3.4.3 2-point value correction
The 2-point value correction makes it possible to perform a
subsequent 2-point correction to achieve higher accuracy for a
larger concentration range.
Note: The 2-point value correction and 2-point matrix correction are
comparable from a calculation perspective.
1. Take several samples on various days with different
concentrations, preferably within a week, and perform an
analysis of the samples in the laboratory. During the time the
samples are being taken, the sample temperature should be
around a maximum of 5 °C, as temperature changes are not
taken into account in the value correction.
Note: The 2-point matrix correction concentrations should be within a
range greater than half a decade. The following formula can assist in the
calculation of the half decade:
2. Make a note of the two values measured with the sensor in the
samples and displayed for the parameters to be corrected
(ammonium and potassium values, or nitrate and chloride
values).
3. Also note the laboratory value measured for ammonium or
nitrate.
All three values form one of the two correction points.
4. Look for two correction points where the laboratory values are
at least half a decade apart and display typical operating
conditions for the installation.
Enter value point
AN–ISE SC NH
4
–N
AN–ISE SC K
Lab value NH
4
–N
Confirm the entry.
1Applies to AN-ISE sc
Calibration
Matrix correction
More corrections
Information
Conc2 >=
Conc1 x 10
2

14 English
Operation
5. Go to the sensor menu and select CALIBRATION > MATRIX
CORRECTION >
2-point value correction and confirm with
ENTER.
6. Select the parameter
1
(NH
4
–N or NO
3
–N) that requires
correction.
Note: When using the AN-ISE sc probe, you can only correct one
parameter at a time. If both parameters need to be corrected, the
procedure must be performed again.
7. Enter the three values for the first correction point and push
CONFIRM THE ENTRY.
Note: The example opposite shows the NH
4
-N and K correction of the
AN-ISE sc probe.
8. To activate the correction, enter the three values for the second
correction point and push
CONFIRM THE ENTRY.
Correction result is shown.
Note: If a correction does not produce a successful result, calculations are
made with the previous correction. After successful completion of value
correction, the corrected value is shown as the display value for ammonium
or nitrate the next time the menu is opened.
4.3.4.4 2-point matrix correction
Proceed as follows to perform 2-point matrix correction:
1. Select
SENSOR MENU > AN-ISE SC or AISE SC or NISE SC >
CALIBRATION > MORE CORRECTIONS
.
2. Select 2-point matrix correction from the selection window
and press
ENTER.
3. Select the Parameter requiring a 2-point matrix correction.
4. Select the point to be corrected.
5.
SELECT Concentration measurement 1 or Concentration
measurement 2
6. Take a water sample from the closest point possible to the
sensor. Filter this sample promptly and perform an immediate
laboratory analysis of the selected parameters. The
measurement value can change very quickly:
When the laboratory value has been determined, proceed as
follows:
7. Select
SENSOR MENU > AN-ISE SC or AISE SC or NISE SC >
CALIBRATE > MORE CORRECTIONS>
2-point matrix
correction
8. Select the parameters to be corrected with the laboratory value
entry:
Enter the values for the
first point
AN–ISE SC NH
4
–N
AN–ISE SC K
Lab value NH
4
–N
Confirm the entry.
Enter the values for the
second point
AN–ISE SC NH
4
–N
AN–ISE SC K
Lab value NH
4
–N
Confirm the entry.
Ammonium
Concentration
measurement 1
Date
Enter the lab value 1.
Concentration
measurement 2
Date
Enter the lab value 2.

English 15
Operation
9. Enter the laboratory reference value and confirm.
The 2-point matrix correction is activated when the entry is
confirmed for both points.

16 English
Section 5 Maintenance
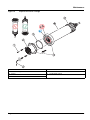
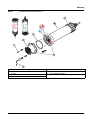
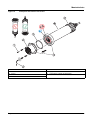
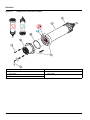
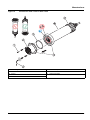
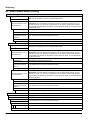
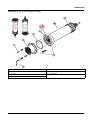
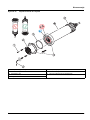
5.3 Replace the sensor cartridge
The sensor cartridge is replaced as described below and in
Figure 15 on page 17.
1. Replace the cartridge using menu item
AN-ISE SC or AISE SC or NISE SC > MAINTENANCE > SERVICE >
CARTRIDGE REPLACEMENT
.
2. Clean the probe and thoroughly dry the sensor cartridge and
probe adapter.
3. Loosen the 4 socket head screws.
.
4. Pull the sensor cartridge out of the probe adapter and discard
the old sensor cartridge as per the applicable regulations.
5. Make sure that a new black gasket is installed every time the
sensor cartridge is replaced. Before the gasket is installed,
clean the surface that faces the cartridge and the groove for the
gasket.
6. Insert the new sensor cartridge into the probe adapter. Observe
the marker hole on the sensor cartridge flange and the probe
adapter.
7. Secure the sensor cartridge with the 4 socket head screws.
8. The sensor code (calibration data) is automatically read for
instruments with automatic recognition (LXG440.99.x000x). For
instruments with non-automatic recognition
(LXG440.99.x001x), enter the new sensor code manually (refer
to certificate).
NOTICE
The sensor cartridge must point downward such that no water can run into
the probe adapter. Pay attention to the contacts between the probe and
the sensor cartridge. These contacts must remain dry.

English 17
Maintenance
Figure 15 Replace the sensor cartridge
1 Socket head screw 5 Union nut
2 Sensor cartridge 6 Marker hole
3 O-ring 7 Socket head wrench
4 Sensor

18 English
Section 6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Error messages
If the sensor is in an error state, the measurement value for this
sensor will flash on the display and the relay contacts and current
outputs associated with this sensor will be stopped. The errors are
described in Table 2.
Table 2 Error messages
Displayed errors Cause Resolution
NH
4
mV is out of range!
1,2
Ammonium mV value exceeds the measurement range
Refer to 6.3.1 Troubleshooting
during operation, Page 21.
K+ mV is out of range!
1,2
Potassium mV value exceeds the measurement range
NO
3
mV is out of range!
1,3
Nitrate mV value exceeds the measurement range
Cl- mV is out of range!
1,3
Chloride mV value exceeds the measurement range
Reference electrode 1
mV is out of range!
REF1 reference value is out of measuring range
Reference electrode 2
mV is out of range!
ORP electrode mV value is out of measuring range
Temperature is out of
range!
Temperature value exceeds measurement range
No cartridge was found. No sensor cartridge connected
Connect the sensor cartridge;
refer to section 3.3, page 15.
Sensor code Sensor code calibration failed
Refer to 6.3.2 Troubleshooting
during calibration, Page 22
Humidity Humidity in the probe Inform service engineer
NH
4
-N concentration is
high.
1,2
Ammonium concentration value exceeds measuring range
Refer to 6.3.1 Troubleshooting
during operation, Page 21.
NH
4
-N concentration is
low.
1,2
Ammonium concentration value is below measuring range
NO
3
-N concentration is
high.
1,3
Nitrate concentration value exceeds measurement range
NO
3
-N concentration is
low.
1,3
Nitrate concentration value is below measurement range
K+ concentration is high.
1,2
Potassium concentration value exceeds measuring range
K+ concentration is low.
1,2
Potassium concentration value is below measuring range
Cl- concentration is high.
1,3
Chloride concentration value exceeds measuring range
Cl- concentration is low.
1,3
Chloride concentration value below measurement range
1
Applies to AN-ISE sc
2
Applies to AISE sc
3
Applies to NISE sc

English 19
Troubleshooting
6.2 Warnings
In the event of a sensor warning, all menus, relays and outputs
continue to function as normal but a warning symbol lights up.
Warnings may be used to activate a relay; users can set warning
levels to define the severity. Warnings are defined in Table 3.
Table 3 Warnings
Displayed warnings Cause Resolution
RFID data Cartridge faulty, read process failed
Replace cartridge, check probe
with test cartridge
NH
4
mV is out of range!
1,2
Ammonium mV value is close to measuring range limit
Refer to 6.3.1 Troubleshooting
during operation, Page 21.
K+ mV is out of range!
1,2
Potassium mV value is close to measuring range limit
NO
3
mV is out of range!
1,3
Nitrate mV value is close to measurement range limit
Cl- mV is out of range!
1,3
Chloride mV value is close to measurement range limit
Reference electrode 1
mV is out of range!
1st reference value is close to limit
Reference electrode 2
mV is out of range!
2nd reference value is close to limit
Temperature is out of
range!
Temperature is close to limit
The cartridge has
expired.
Sensor cartridge more than 1 year old Replace the sensor cartridge
NH
4
-N concentration is
high.
1,2
Ammonium concentration value exceeds measuring range
See 6.3.1 Troubleshooting during
operation, Page 21.
NH
4
-N concentration is
low.
1,2
Ammonium concentration value is below measuring range
NO
3
-N concentration is
high.
1,3
Nitrate concentration value exceeds measuring range
NO
3
-N concentration is
low.
1,3
Nitrate concentration value is below measurement range
K+ concentration is high.
1,2
Potassium concentration value exceeds measuring range
K+ concentration is low.
1,2
Potassium concentration value is below measuring range
Cl- concentration is high.
1,3
Chloride concentration value exceeds measuring range
Cl- concentration is low.
1,3
Chloride concentration value is below measurement range

20 English
Troubleshooting
Ammonium
1,2
Refer to 6.3.2 Troubleshooting
during calibration, Page 22.
Offset Ammonium offset exceeds measurement range
Slope Ammonium slope exceeds measurement range
Potassium
1,2
Offset Potassium offset exceeds measurement range
Slope Potassium slope is out of measuring range
Nitrate
Offset Nitrate offset is out of measurement range
Slope Nitrate slope is out of measurement range
Chloride
Offset Chloride offset is out of measurement range
Slope Chloride slope is out of measurement range
1
Applies to AN-ISE sc
2
Applies to AISE sc
3
Applies to NISE sc
Table 3 Warnings
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
La pagina si sta caricando...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
-
 135
135
-
 136
136
-
 137
137
-
 138
138
-
 139
139
-
 140
140
-
 141
141
-
 142
142
-
 143
143
-
 144
144
-
 145
145
-
 146
146
-
 147
147
-
 148
148
-
 149
149
-
 150
150
-
 151
151
-
 152
152
Hach NISE sc Addendum To The Operator Manual
- Tipo
- Addendum To The Operator Manual
in altre lingue
- English: Hach NISE sc
- français: Hach NISE sc
- español: Hach NISE sc
- Deutsch: Hach NISE sc
- Nederlands: Hach NISE sc
- dansk: Hach NISE sc
- polski: Hach NISE sc
Documenti correlati
Altri documenti
-
CARLO GAVAZZI UA 30 CLD**F.M7 Manuale utente
-
CARLO GAVAZZI UA 30 CLD**F.M7 Manuale utente
-
Trane DFS 4 Technical Manual
-
Trane WFS 3 Technical Manual
-
Trane FCAE Technical Manual
-
Trane FVAS Technical Manual
-
Varian Saturn 2000 GC/MS Manuale utente
-
Trane WFE 2 Technical Manual
-
ONKYO TX-NR 717 Manuale utente
-
YSI PRO PLUS Manuale del proprietario


























































































































































